Getting a roof over your head — a long dream
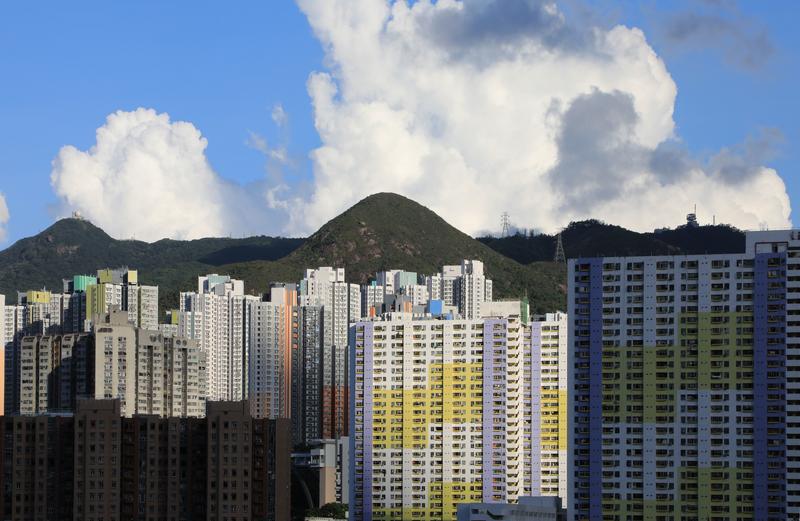


According to Our Hong Kong Foundation, construction work for up to 75 percent of public housing units built between 2015 and 2020 had to be delayed. Over the next four years, 21,800 units on average are due to be completed — still nearly 30 percent short of the government's target.
In the latest Long Term Housing Strategy report, the government said it plans to build 316,000 public housing apartments over the next decade, with two-thirds of them to be completed after 2026.
Former Hong Kong chief executive Leung Chun-ying said in May that Hong Kong's civil servants lack a sense of urgency in dealing with housing-related projects, alleging it could easily take weeks for a document to be circulated and signed by the necessary departments.
"We have failed to adopt a 'do it or die' attitude. We really need to race against time to solve Hong Kong's housing problem … and we must provide public housing as early as possible for those still living in subdivided flats," said Leung, who is now a vice-chairman of the National Committee of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference, the country's top political advisory body.
Chief Executive Carrie Lam Cheng Yuet-ngor has acknowledged the deficiency in administrative and regulatory procedures, adding that civil servants are willing to accept criticism. "But every administration has its own strategy in terms of land supply," she said.
Leung also called for the revival of a plan to develop country parks into public housing estates — an idea proposed near the end of his tenure as chief executive but later shelved by the current administration.
He suggested that up to 25,000 public housing units could be built on the fringes of Tai Lam Country Park in the northwestern New Territories, covering 70 hectares, or less than 0.2 percent of the total area of the city's country parks.
The new homes could be sold at HK$6,000 per square foot, he said, adding that authorities should consider developing construction plans and inviting applications from residents simultaneously to expedite the process.
"We believe the focus of our housing policy should be to find more land in the long run, instead of just changing the use of land," said Lam, adding that turning country parks into housing estates is very likely to spark discontent and opposition among affected neighborhoods.
"Different housing policies will have different outcomes. You cannot judge (the effects) simply by speed. The effects of land policies are not immediate in most cases. If you only evaluate the figures at a certain point, the conclusion you come to could be biased," she argued.
Leung said, "I'm not against other plans to increase land supply, but I hope my suggestions won't be ignored. We need to give Hong Kong people, especially young families, the hope of owning a flat."
Wong, the development chief, said developing country parks is not an immediate option, noting that the plan had "failed to get majority support" from the public in 2018. However, the government could reconsider it "at an appropriate time", he added.
He estimated the government could recover 100 hectares of land annually in the next five years, compared with 4 hectares each year from 2014 to 2019.
The Development Bureau said in May that three private parcels of land in the New Territories, covering a total of 12,300 square meters, would be resumed under the Lands Resumption Ordinance to build 1,600 subsidized apartments.
- From muggles to birders, quiet hobby finds its wings
- Two-way tourism between China, Europe gathers pace over May holiday
- Nanjing Massacre survivor Liu Guixiang dies
- Macao's resident deposits rise in March
- Taiwan youth seek their career in Chinese mainland
- Xi urges youth to contribute to Chinese modernization