A gripping mystery
One of the biggest questions that still confounds Sanxingdui experts is: What did the bronze standing man once hold in his hands? Zhao Xu feels around for answers.
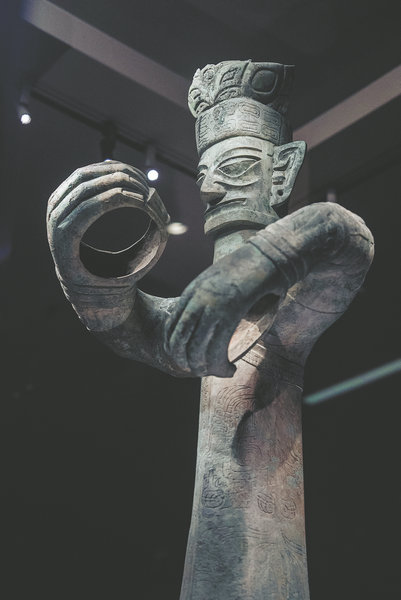


The gold scepter
"A gold scepter — this is one of the earliest suggested answers," says Hu Jialin, who's behind a well-researched ongoing exhibition at the newly opened Shanghai Museum East, which takes a deeper look at the myths surrounding the ancient civilization of Sanxingdui.
The reason is simple: barely a month before the discovery of the bronze man in August 1986, a 1.42-meter-long gold scepter was unearthed from the site. Weighing about half a kilogram, the scepter was made up of a layer of gold foil wrapped around a wooden stick. With its wooden core long rotted away, the gold scepter, so rumpled that it was initially thought to be a belt, has proved to be one of the biggest of its kind found in China, as well as the rest of the world.
Together with other gold items, including a giant gold foil mask weighing more than 280 grams that was excavated from the site in 2020, the scepter has fueled speculation that the Sanxingdui culture — and the ancient kingdom behind it — had shared direct ties with the far-flung lands to its west, including ancient Mesopotamia and Egypt, where gold was the material of choice for the ruling class, and scepters were a recognized symbol of power.
"But there's one fundamental problem: If the tradition of gold making and usage had indeed traveled for thousands of kilometers from the Near East to the Chengdu Plain, where the Sanxingdui culture had prospered, it couldn't have done it alone. In other words, there must have been something else, major crops or even written languages for example, that had made the same journey, of which we haven't yet found any evidence," says Hu, referring to the absence in Sanxingdui of archaeological wheat remains, wheat being cultivated in the Near East at the time.
"In sharp contrast, we have discovered the archaeological remains of millet and rice, grown at the time in the Yellow River basin and the Yangtze River Delta region, respectively."
In the 1980s, Chinese archaeologist Tong Enzheng (1935-1997) came up with his model of a crescent-shaped exchange belt extending from China's northeast to its southwest, arching midway toward the Mongolian steppes and the eastern rim of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Along this belt, the decrease of latitude is compensated by the increase of altitude, resulting in a roughly similar annual average temperature, precipitation and vegetation for this long stretch of land.
China's Arc — that is the term used by world-renowned British art historian and Sinologist Jessica Rawson to describe the region, on the lower southwestern section of which Sanxingdui is located.
"Sharing more similarities than differences, the various nomadic cultures dispersed along this extended belt tended to have more exchanges with one another than with the agrarian societies located to their east," says Hu.
"In my view, the gold tradition of Sanxingdui probably had something to do with the steppe cultures in East Asia, which prized gold and had long worked with the material," he says, conveniently pointing out that, although metal casting appeared in the West approximately 1,000 years earlier than it did in China, it was very unlikely to have influenced the bronze-making of Sanxingdui.
"While arsenical bronze — copper with a large percentage of arsenic — was widely used in the West, the Sanxingdui relics were made using leaded tin bronze, which has a lower melting point and therefore higher fluidity, allowing for the casting of intricate details, exemplified by the bronze items created during China's Shang Dynasty (c. 16th century-11th century BC)."